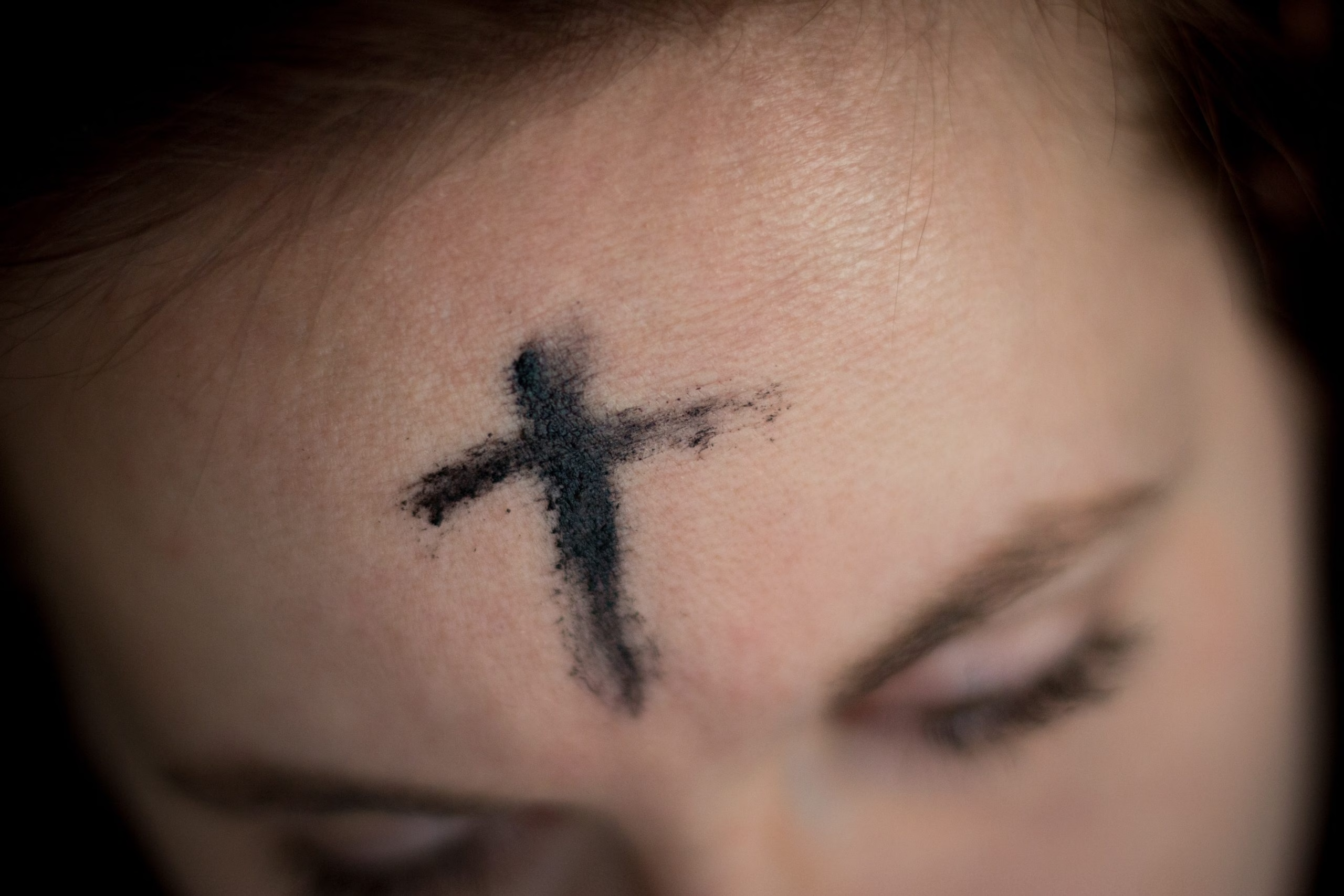William Johnston, University of Dayton
For Christians, the death and resurrection of Jesus is a pivotal event commemorated each year during a season of preparation called Lent and a season of celebration called Easter.
The day that begins the Lenten season is called Ash Wednesday. Here are four things to know about it.
1. Origin of the tradition of using ashes
On Ash Wednesday, many Christians have ashes put on their forehead – a practice that has been going on for about a thousand years.
In the earliest Christian centuries – from A.D. 200 to 500 – those guilty of serious sins such as murder, adultery or apostasy, a public renunciation of one’s faith, were excluded for a time from the Eucharist, a sacred ceremony celebrating communion with Jesus and with one another.
During that time they did acts of penance, like extra praying and fasting, and lying “in sackcloth and ashes,” as an outward action expressing interior sorrow and repentance.
The customary time to welcome them back to the Eucharist was at the end of Lent, during Holy Week.
But Christians believe that all people are sinners, each in his or her own way. So as centuries went on, the church’s public prayer at the beginning of Lent added a phrase, “Let us change our garments to sackcloth and ashes,” as a way to call the whole community, not just the most serious sinners, to repentance.
Around the 10th century, the practice arose of acting out those words about ashes by actually marking the foreheads of those taking part in the ritual. The practice caught on and spread, and in 1091 Pope Urban II decreed that “on Ash Wednesday everyone, clergy and laity, men and women, will receive ashes.” It’s been going on ever since.
2. Words used when applying ashes
A 12th-century missal, a ritual book with instructions on how to celebrate the Eucharist, indicates the words used when putting ashes on the forehead were: “Remember, man, that you are dust and to dust you shall return.” The phrase echoes God’s words of reproach after Adam, according to the narrative in the Bible, disobeyed God’s command not to eat from the tree of the knowledge of good and evil in the Garden of Eden.
This phrase was the only one used on Ash Wednesday until the liturgical reforms following the Second Vatican Council in the 1960s. At that time a second phrase came into use, also biblical but from the New Testament: “Repent, and believe in the Gospel.” These were Jesus’s words at the beginning of his public ministry, that is, when he began teaching and healing among the people.
Each phrase in its own way serves the purpose of calling the faithful to live their Christian lives more deeply. The words from Genesis remind Christians that life is short and death imminent, urging focus on what is essential. The words of Jesus are a direct call to follow him by turning away from sin and doing what he says.
3. Two traditions for the day before
Two quite different traditions developed for the day leading up to Ash Wednesday.
One might be called a tradition of indulgence. Christians would eat more than usual, either as a final binge before a season of fasting or to empty the house of foods typically given up during Lent. Those foods were chiefly meat, but depending on culture and custom, also milk and eggs and even sweets and other forms of dessert food. This tradition gave rise to the name “Mardi Gras,” or Fat Tuesday.
The other tradition was more sober: namely, the practice of confessing one’s sins to a priest and receiving a penance appropriate for those sins, a penance that would be carried out during Lent. This tradition gave rise to the name “Shrove Tuesday,” from the verb “to shrive,” meaning to hear a confession and impose a penance.
In either case, on the next day, Ash Wednesday, Christians dive right into Lenten practice by both eating less food overall and avoiding some foods altogether.
4. Ash Wednesday has inspired poetry
In 1930s England, when Christianity was losing ground among the intelligentia, T.S. Eliot’s poem “Ash Wednesday” reaffirmed traditional Christian faith and worship. In one section of the poem, Eliot wrote about the enduring power of God’s “silent Word” in the world:
If the lost word is lost, if the spent word is spent If the unheard, unspoken Word is unspoken, unheard; Still is the unspoken word, the Word unheard, The Word without a word, the Word within The world and for the world; And the light shone in darkness and Against the Word the unstilled world still whirled About the centre of the silent Word.
Ellen Garmann, Associate Director of Campus Ministry for Liturgy at University of Dayton, contributed to this piece.
William Johnston, Associate Professor of Religious Studies, University of Dayton
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.